BLOG

There have recently been several web forum and group discussions about photo type and relevance to skin analysis, and during these discussions there appeared to be for some participants, a rudimentary understanding of the importance of this characteristic in professional skin analysis. The purpose of this primer is to provide a good base of understanding. […]
The post The importance of Photo type & Risk Assessment appeared first on Pastiche.

It’s Ironic that many people spend a lot of time and money on skin care products for their sensitive, reactive skin, but don’t consider that same amount of money, care, and thought be given to the shampoo, conditioner, and colour frequently applied to their scalp and hair.As professional skin treatment therapists, could we be doing […]
The post Is Hair Care Affecting Your Skin Health? appeared first on Pastiche.
Dermatological, Cosmeceutical and Corneotherapy:The difference explained There is perhaps equal measures of misunderstanding and misconception regarding the grades of skincare products, particularly when the formulations approach dermatological effects.This is not helped when new marketing terms are invented to imply performance. In this article we will look at the definition of the two main classes of […]
The post Dermatological, Cosmeceutical and Corneotherapy: The difference explained appeared first on Pastiche.
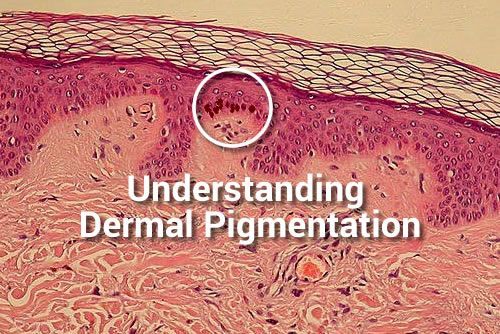
Commonly misunderstood within the skin treatment /specialist professions, is the term Dermal Pigmentation, and it is appropriate that some clarity and thought to the subject be considered. I have already published the basics on the topic of melanogenesis and want to reiterate that the formation of skin pigment is an Epidermal event NOT Dermal, and […]
The post Understanding Dermal Pigmentation appeared first on Pastiche.
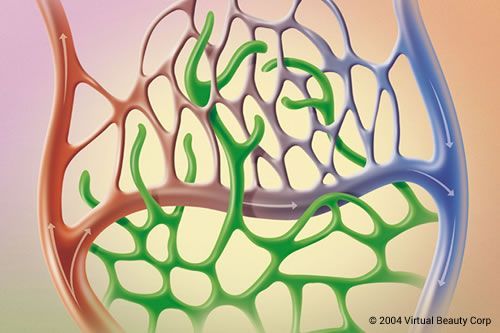
Broken capillaries: fact or fiction? The objective of this blog is to raise the awareness of teachers, educational bodies, and distributors to the medical and skin treatment industry of how teaching incorrect, supersededor redundant information results in a knowledge base that has no relevance to the current times. The old language of ‘broken capillaries’ being […]
The post Broken capillaries: fact or fiction? appeared first on Pastiche.
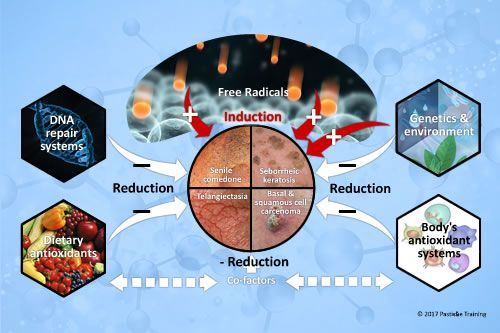
Why do many ageing skins develop comedones and other keratolytic disorders?There is now universal agreement that free radicals are involved in the physical, biochemical, and pathological changes associated with aging. Oxidative damage to proteins, lipids, and DNA accumulates and increases with age, and is associated with age-related skin conditions, disorders and diseases. In mature skins, […]
The post Ageing skins, comedones and other keratolytic disorders appeared first on Pastiche.

Some 15 years after I originally wrote this article, I still come across therapists and aestheticians practicing somewhat “outdated” techniques and procedures related to the humble application of the mask. I’ve revived it once more; as both a reminder and a wake-up call to the educators who are still teaching largely obsolete practices. The treatment […]
The post New procedures for old Treatments appeared first on Pastiche.
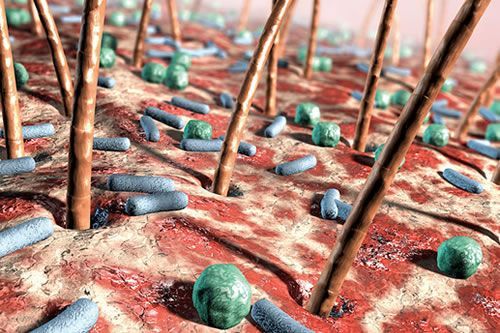
I have often said that many of the modern skin conditions/disorders of today are caused by over treatment and/or over cleansing by the patient. This cleansing habit combined with the poor quality emulsifiers that are used in some cosmetics and the daily application of antibacterial substances has led to situations where the adaptive immune system […]
The post The Importance of the Skin Surface Microflora appeared first on Pastiche.

In an earlier one of my ‘Flo says’ publications,we talked about hydration treatments and mentioned a little about how the relevant ambient humidity can affect the results of a treatment. I oftensay in class that you have to think like a ‘weather presenter’ and consider if the treatment is seasonally appropriate or if the correct […]
The post Environmental Defense Treatments for Summer appeared first on Pastiche.


